- What Is Adhesive Tape?
- What Are Adhesive Tapes Made Of?
- How Are Adhesive Tapes Applied?
- Most Popular Types Of Adhesive Tapes.
- What Types Of Adhesives Are Used For Tapes?
- Which Materials Are Used For The Backing Or Carrier?
What Is Adhesive Tape?
Adhesive tapes is a combination of a material and an adhesive film and used to bond or join objects together instead of using fasteners, screws, or welding. Applying adhesive tapes in lieu of mechanical fasteners enables you to use lower temperature applications, which can simplify the manufacturing processes. Additionally, adhesive tapes can protect your surface area since there is no need to damage the surface by using fasteners or screws. Adhesive tapes are great solutions for automated product production, whereas liquid adhesives are messy and time-consuming because they need to be sprayed or rolled onto the surface before bonding takes place.
What Are Adhesive Tapes Made Of?
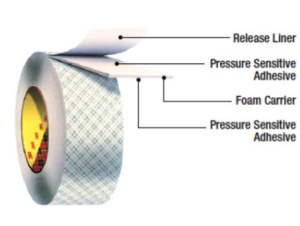
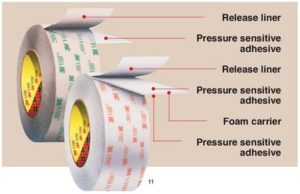
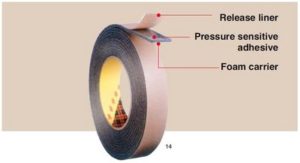
Adhesive tapes consist of a material called a backing or carrier (paper, plastic film, cloth, foam, foil, etc.), which is coated with an adhesive and a release liner if needed. The adhesive-coated backing or carrier is then wound up to form a long jumbo roll of tape. The jumbo roll is then slit into narrow width bands to produce several rolls of tape. Each roll and its composition are unique and can be tailored to specific applications for a wide variety of bonding solutions.
How Are Adhesive Tapes Applied?
Adhesive tapes can be pressure sensitive, thermally activated or may even require moisture to work. Others, such as latex gums, adhere to themselves.
Most Popular Types Of Adhesive Tapes:
- Pressure sensitive adhesives (PSAs) are tacky at room temperature in dry form. They adhere firmly to a variety of surfaces and require only the application of a finger or hand. PSAs do not require water, solvent or heat activation in order to bond to materials such as paper, plastic, glass, wood, cement and metal. The recommended bonding pressure is 14.5 – 29 psi =^ 10 – 20 N/cm². The temperature during application should be moderate, somewhere between 59º F and 95º F. Lower temperatures might lead to insufficient “wetting” or “coverage” of the adhesive on the substrate. Very high temperatures may cause the tape to stretch when being applied, which could create additional stress in the final application.
- Heat activated tape is usually tack-free until it is activated by a heat source. Heat activated tape requires time at elevated temperatures at 180˚F or higher to achieve a bond. Heat-activated adhesive allows for aggressive bonding to difficult surfaces such as rubber, EPDM, PU and PVC-based plastic materials. It can be made with different carriers that are suitable for a variety of applications.
- Water activated tape, gummed paper tape or gummed tape is a starch or an animal glue-based adhesive on a kraft paper backing which becomes sticky when moistened. Water activated tape is inexpensive and is used for closing and sealing boxes.
- Non-adhesive tapes, films or laminates do not have an applied adhesive because they are self-adhering. PTFE thread-sealing tape is a type of non-adhesive tape.
What Types Of Adhesives Are Used For Tapes?
Selecting the right adhesive for your project requires a good understanding of the application and backing or carrier being used.
- Acrylic adhesives provide excellent environmental resistance and provide a faster setting time than other adhesives.
- Epoxy resins exhibit high strength and low shrinkage during curing and are known for their toughness and resistance to chemical and environmental damage.
- Rubber-based adhesives provide highly flexible bonds and are usually based on butadiene-styrene, butyl, polyisobutylene or nitrile compounds.
- Silicone adhesives and sealants have a high degree of flexibility and are resistant to very high temperatures.
- Polyurethane and Isocyanate adhesives provide more flexibility, impact, resistance, and durability.
Which Materials Are Used For The Backing Or Carrier?
Adhesive tapes and films vary in terms of a carrier or backing material. Here are the most common backings/carriers.
- Paper: Paper tape products have a paper backing and are also referred as flat back tape.
- Cloth: A cloth backing often incorporates a woven cloth or a fabric layer for reinforcement, extra strength and heat resistance properties.
- Felt: Felt or non-woven tapes are often applied to substrates to prevent scratching.
- Foam: Adhesive-coated foam backing tape contains an adhesive that is protected by a liner. Foam is often used for sealing, weather-stripping, and mounting.
- Metal Foil: Aluminum, aluminum-reinforced and lead backings resist flames, temperature extremes, and high humidity. Metal tapes are usually designed for taping joints and seams against moisture or vapor. Aluminum foil is laminated to paper or plastic films to provide more strength. Copper foil backing is used in the manufacture of multilayer printed circuit boards (PCB).
- Plastic Film/Polymer: Generally, there are two categories of plastics: thermoplastics and thermosets. Plastic products contain one or more plastic layers. They consist of a plastic film that can be clear, colored, printed or plain. They can be single-layered or multilayered, and combined with materials such as paper and/or aluminum.
- PET/Polyester: Polyethylene teraphthalate (PET)/polyester products use a PET or polyester backing in the form of a film or laminate. Also known as Mylar.
- Polyimide: Polyimide tape consists of a polyimide film and a heat-resistant, silicone adhesive. Polyimide films are useful substrates for the manufacture of flexible circuit materials. Polyimide film maintains excellent physical, mechanical, chemical and electrical properties over a wide range of environments. (Also known and branded as Kapton Tape)
- PVC/Vinyl: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)/vinyl products use a vinyl or PVC backing to resist wear, weathering, and abrasion.
- Rubber: Rubber backing can be used to produce a conformable self-fusing rubber electrical insulating and sealing tape.
- Silicone: Silicone is a superior product for gaskets, insulators, press pads, and die-cut parts. Many grades of silicone backing can be used to match varying requirements.
- Acrylic Films: Acrylic films are plastic or thermoplastic resin films manufactured using polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) or polymethyl-2-methylpropanoate. Acrylic films have excellent clarity and are UV stable.
- Glass/Fiberglass: Fiberglass composite material or a glass layer provides exceptional stability in harsh environments by resisting shrinking, rotting, or burning.
- Filament: Filament tape, usually referred to as strapping tape, is composed of thousands of filaments (usually fiberglass) woven into yarns that are embedded into the adhesive. It is a strong and versatile material that allows the user to bundle similar or odd-shaped items together for shipping or storage.
- Fluoropolymer/PTFE/PVDF: Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is an insoluble compound that exhibits a high degree of chemical resistance and a low coefficient of friction. Fluoropolymer films, layers or coatings consist of plastics such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). Fluoropolymer is often used in applications that require superior chemical resistance, good dielectric properties and water and stain repellent characteristics. It’s also used in applications where the material handled must not stick to the belt, fabric or laminate.
- Films are synthetic resin adhesives that can include a carrier, but not all do.
- Transfer tape, a highly versatile product, consists of a thin adhesive film with no carrier and can be transferred to most dry surfaces as a peel-away release liner. Transfer tapes often use a release liner to improve handling and dispensing of the tape.
- Double-sided tape liners often incorporate differentially coated release liners that are easy to peel. These release liners are made either of paper, film or silicone.
Now that you have a better understanding of how different materials and adhesives can be combined to create tapes and that the invention of tape will rule the world, give us a call at 1-800-643-5996 and one of our Adhesive Tape specialists will help you build your customized tape solution.
It’s More Than Tape. We Convert Your Ideas into Reality.
<< Tape >> << Tape History >>